16 KiB
| layout | title | parent | nav_order |
|---|---|---|---|
| default | Objectron (3D Object Detection) | Solutions | 11 |
MediaPipe Objectron
{: .no_toc }
Table of contents
{: .text-delta } 1. TOC {:toc}Overview
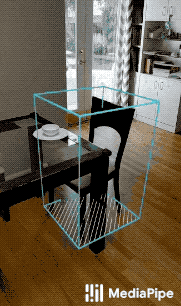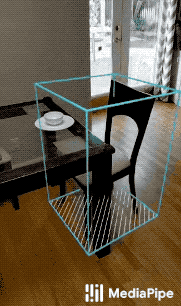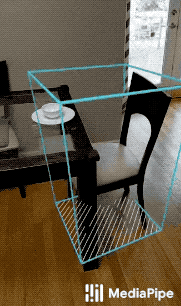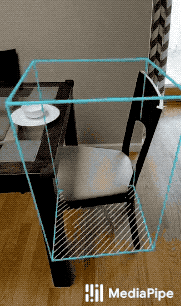
MediaPipe Objectron is a mobile real-time 3D object detection solution for everyday objects. It detects objects in 2D images, and estimates their poses through a machine learning (ML) model, trained on the Objectron dataset.
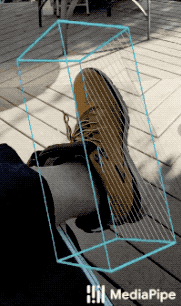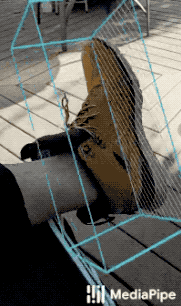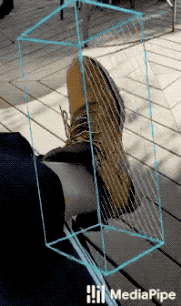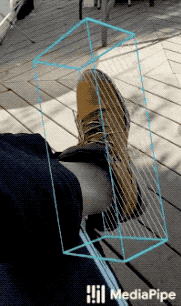 |
 |
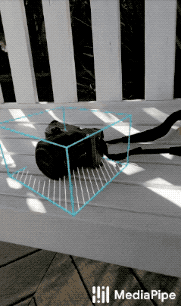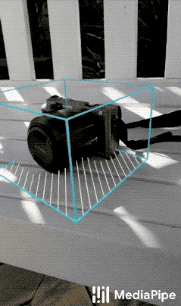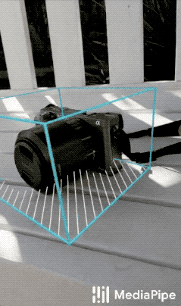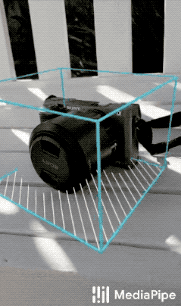 |
 |
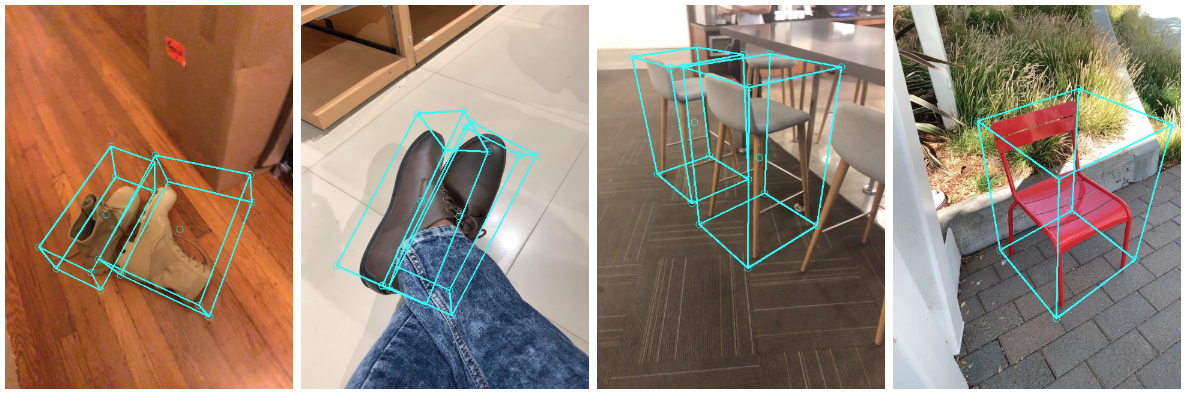
|---|---|---|---|
| Fig 1a. Shoe Objectron | Fig 1b. Chair Objectron | Fig 1c. Camera Objectron | Fig 1d. Cup Objectron |
Object detection is an extensively studied computer vision problem, but most of the research has focused on 2D object prediction. While 2D prediction only provides 2D bounding boxes, by extending prediction to 3D, one can capture an object’s size, position and orientation in the world, leading to a variety of applications in robotics, self-driving vehicles, image retrieval, and augmented reality. Although 2D object detection is relatively mature and has been widely used in the industry, 3D object detection from 2D imagery is a challenging problem, due to the lack of data and diversity of appearances and shapes of objects within a category.
 |
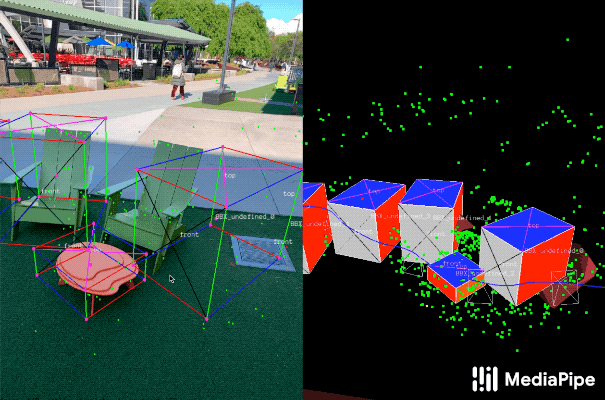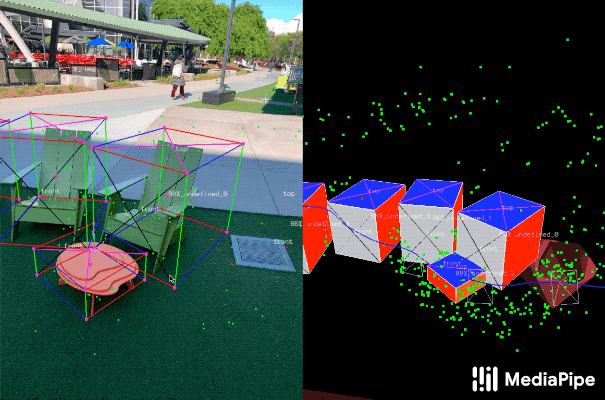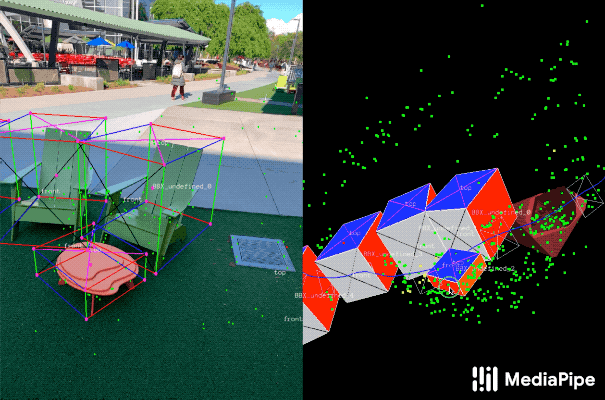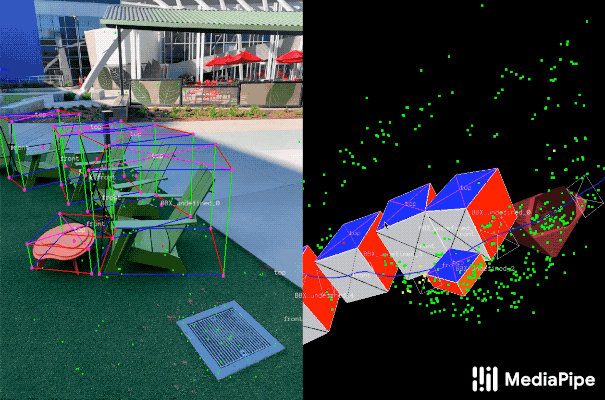
|---|
| Fig 2. Objectron example results. |
Obtaining Real-World 3D Training Data
While there are ample amounts of 3D data for street scenes, due to the popularity of research into self-driving cars that rely on 3D capture sensors like LIDAR, datasets with ground truth 3D annotations for more granular everyday objects are extremely limited. To overcome this problem, we developed a novel data pipeline using mobile augmented reality (AR) session data. With the arrival of ARCore and ARKit, hundreds of millions of smartphones now have AR capabilities and the ability to capture additional information during an AR session, including the camera pose, sparse 3D point clouds, estimated lighting, and planar surfaces.
In order to label ground truth data, we built a novel annotation tool for use with AR session data, which allows annotators to quickly label 3D bounding boxes for objects. This tool uses a split-screen view to display 2D video frames on which are overlaid 3D bounding boxes on the left, alongside a view showing 3D point clouds, camera positions and detected planes on the right. Annotators draw 3D bounding boxes in the 3D view, and verify its location by reviewing the projections in 2D video frames. For static objects, we only need to annotate an object in a single frame and propagate its location to all frames using the ground truth camera pose information from the AR session data, which makes the procedure highly efficient.
AR Synthetic Data Generation
A popular approach is to complement real-world data with synthetic data in order to increase the accuracy of prediction. However, attempts to do so often yield poor, unrealistic data or, in the case of photorealistic rendering, require significant effort and compute. Our novel approach, called AR Synthetic Data Generation, places virtual objects into scenes that have AR session data, which allows us to leverage camera poses, detected planar surfaces, and estimated lighting to generate placements that are physically probable and with lighting that matches the scene. This approach results in high-quality synthetic data with rendered objects that respect the scene geometry and fit seamlessly into real backgrounds. By combining real-world data and AR synthetic data, we are able to increase the accuracy by about 10%.
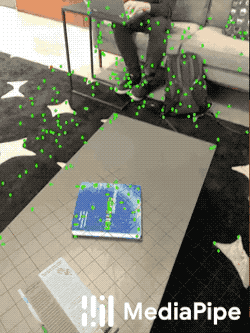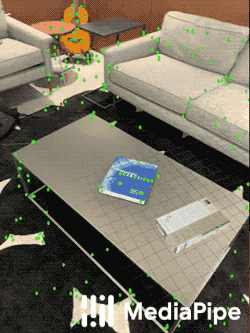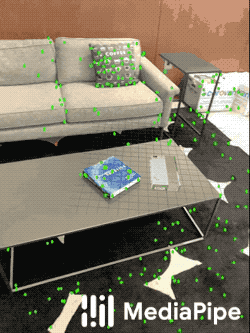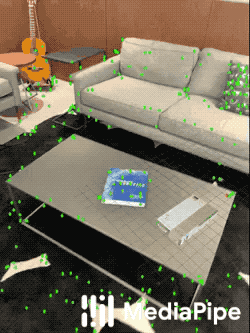 |
|---|
| Fig 4. An example of AR synthetic data generation. The virtual white-brown cereal box is rendered into the real scene, next to the real blue book. |
ML Pipelines for 3D Object Detection
We built two ML pipelines to predict the 3D bounding box of an object from a single RGB image: one is a two-stage pipeline and the other is a single-stage pipeline. The two-stage pipeline is 3x faster than the single-stage pipeline with similar or better accuracy. The single stage pipeline is good at detecting multiple objects, whereas the two stage pipeline is good for a single dominant object.
Two-stage Pipeline
Our two-stage pipeline is illustrated by the diagram in Fig 5. The first stage uses an object detector to find the 2D crop of the object. The second stage takes the image crop and estimates the 3D bounding box. At the same time, it also computes the 2D crop of the object for the next frame, such that the object detector does not need to run every frame.
 |
|---|
| Fig 5. Network architecture and post-processing for two-stage 3D object detection. |
We can use any 2D object detector for the first stage. In this solution, we use TensorFlow Object Detection trained with the Open Images dataset. The second stage 3D bounding box predictor we released runs 83FPS on Adreno 650 mobile GPU.
Single-stage Pipeline
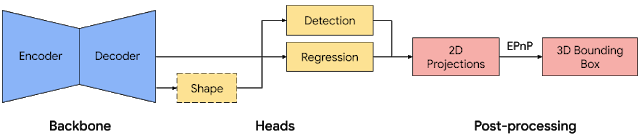 |
|---|
| Fig 6. Network architecture and post-processing for single-stage 3D object detection. |
Our single-stage pipeline is illustrated by the diagram in Fig 6, the model backbone has an encoder-decoder architecture, built upon MobileNetv2. We employ a multi-task learning approach, jointly predicting an object's shape with detection and regression. The shape task predicts the object's shape signals depending on what ground truth annotation is available, e.g. segmentation. This is optional if there is no shape annotation in training data. For the detection task, we use the annotated bounding boxes and fit a Gaussian to the box, with center at the box centroid, and standard deviations proportional to the box size. The goal for detection is then to predict this distribution with its peak representing the object’s center location. The regression task estimates the 2D projections of the eight bounding box vertices. To obtain the final 3D coordinates for the bounding box, we leverage a well established pose estimation algorithm (EPnP). It can recover the 3D bounding box of an object, without a priori knowledge of the object dimensions. Given the 3D bounding box, we can easily compute pose and size of the object. The model is light enough to run real-time on mobile devices (at 26 FPS on an Adreno 650 mobile GPU).
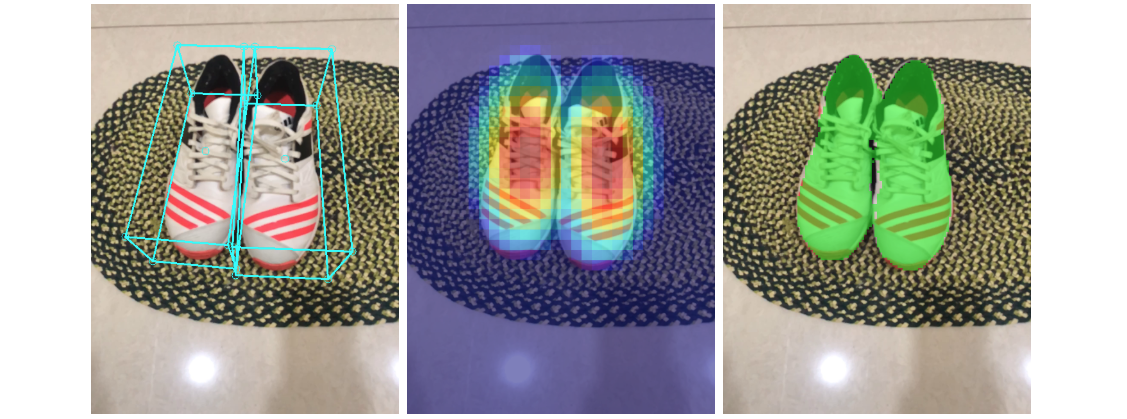 |
|---|
| Fig 7. Sample results of our network — (Left) original 2D image with estimated bounding boxes, (Middle) object detection by Gaussian distribution, (Right) predicted segmentation mask. |
Detection and Tracking
When the model is applied to every frame captured by the mobile device, it can suffer from jitter due to the ambiguity of the 3D bounding box estimated in each frame. To mitigate this, we adopt the same detection+tracking strategy in our 2D object detection and tracking pipeline in MediaPipe Box Tracking. This mitigates the need to run the network on every frame, allowing the use of heavier and therefore more accurate models, while keeping the pipeline real-time on mobile devices. It also retains object identity across frames and ensures that the prediction is temporally consistent, reducing the jitter.
The Objectron 3D object detection and tracking pipeline is implemented as a MediaPipe graph, which internally uses a detection subgraph and a tracking subgraph. The detection subgraph performs ML inference only once every few frames to reduce computation load, and decodes the output tensor to a FrameAnnotation that contains nine keypoints: the 3D bounding box's center and its eight vertices. The tracking subgraph runs every frame, using the box traker in MediaPipe Box Tracking to track the 2D box tightly enclosing the projection of the 3D bounding box, and lifts the tracked 2D keypoints to 3D with EPnP. When new detection becomes available from the detection subgraph, the tracking subgraph is also responsible for consolidation between the detection and tracking results, based on the area of overlap.
Objectron Dataset
We also released our Objectron dataset, with which we trained our 3D object detection models. The technical details of the Objectron dataset, including usage and tutorials, are available on the dataset website.
Example Apps
Please first see general instructions for Android and iOS on how to build MediaPipe examples.
Note: To visualize a graph, copy the graph and paste it into MediaPipe Visualizer. For more information on how to visualize its associated subgraphs, please see visualizer documentation.
Two-stage Objectron
-
Graph:
mediapipe/graphs/object_detection_3d/object_occlusion_tracking.pbtxt -
Android target:
mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3d.Build for shoes (default) with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3dBuild for chairs with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 --define chair=true mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3dBuild for cups with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 --define cup=true mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3dBuild for cameras with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 --define camera=true mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3d -
iOS target: Not available
Single-stage Objectron
-
Graph:
mediapipe/graphs/object_detection_3d/object_occlusion_tracking_1stage.pbtxt -
Android target:
mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3d.Build with single-stage model for shoes with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 --define shoe_1stage=true mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3dBuild with single-stage model for chairs with: (or download prebuilt ARM64 APK)
bazel build -c opt --config android_arm64 --define chair_1stage=true mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/objectdetection3d:objectdetection3d -
iOS target: Not available
Resources
- Google AI Blog: Announcing the Objectron Dataset
- Google AI Blog: Real-Time 3D Object Detection on Mobile Devices with MediaPipe
- Paper: MobilePose: Real-Time Pose Estimation for Unseen Objects with Weak Shape Supervision
- Paper: Instant 3D Object Tracking with Applications in Augmented Reality (presentation)
- Models and model cards