5.3 KiB
| layout | target | title | parent | grand_parent | nav_order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| forward | https://developers.google.com/mediapipe/ | MediaPipe Android Solutions | MediaPipe on Android | Getting Started | 2 |
MediaPipe Android Solutions
{: .no_toc }
- TOC {:toc}
Attention: Thanks for your interest in MediaPipe! We have moved to https://developers.google.com/mediapipe as the primary developer documentation site for MediaPipe as of April 3, 2023.
MediaPipe Android Solution APIs (currently in alpha) are available in:
Incorporation in Android Studio
Prebuilt packages of Android Solution APIs can be found in Google's Maven Repository. To incorporate them into an Android Studio project, add the following into the project's Gradle dependencies:
dependencies {
// MediaPipe solution-core is the foundation of any MediaPipe Solutions.
implementation 'com.google.mediapipe:solution-core:latest.release'
// Optional: MediaPipe Face Detection Solution.
implementation 'com.google.mediapipe:facedetection:latest.release'
// Optional: MediaPipe Face Mesh Solution.
implementation 'com.google.mediapipe:facemesh:latest.release'
// Optional: MediaPipe Hands Solution.
implementation 'com.google.mediapipe:hands:latest.release'
}
If you need further customization, instead of using the prebuilt maven packages consider building a MediaPipe Android Archive library locally from source by following these instructions.
Building solution example apps
Detailed usage examples of the Android Solution APIs can be found in the source code of the solution example apps.
To build these apps:
-
Open Android Studio Arctic Fox on Linux, macOS, or Windows.
-
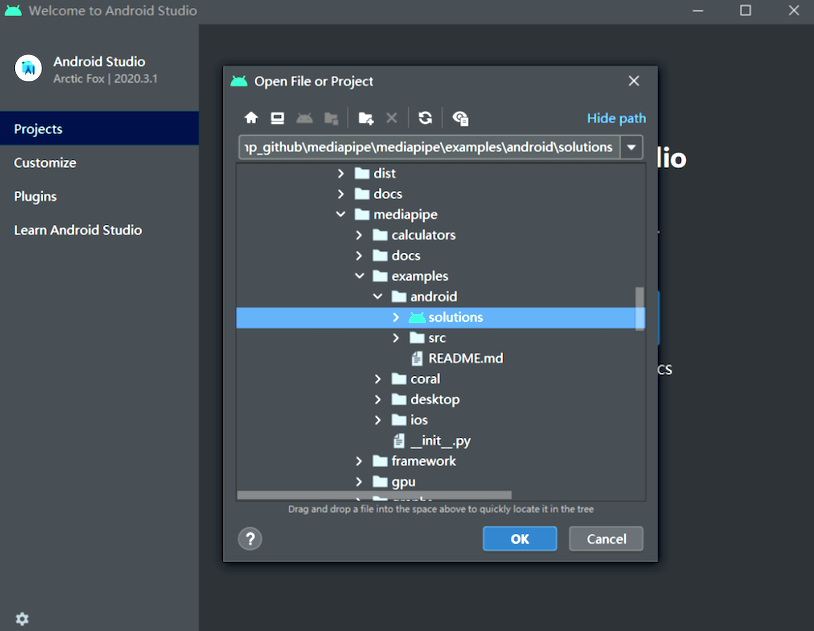
Import mediapipe/examples/android/solutions directory into Android Studio.
-
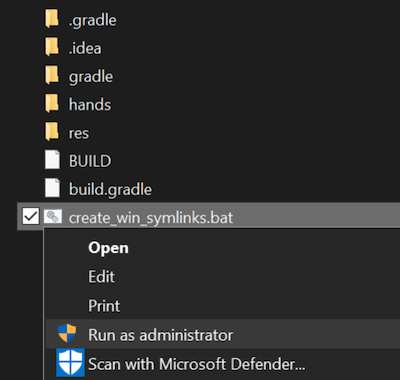
For Windows users, run
create_win_symlinks.batas administrator to create res directory symlinks. -
Select "File" -> "Sync Project with Gradle Files" to sync project.
-
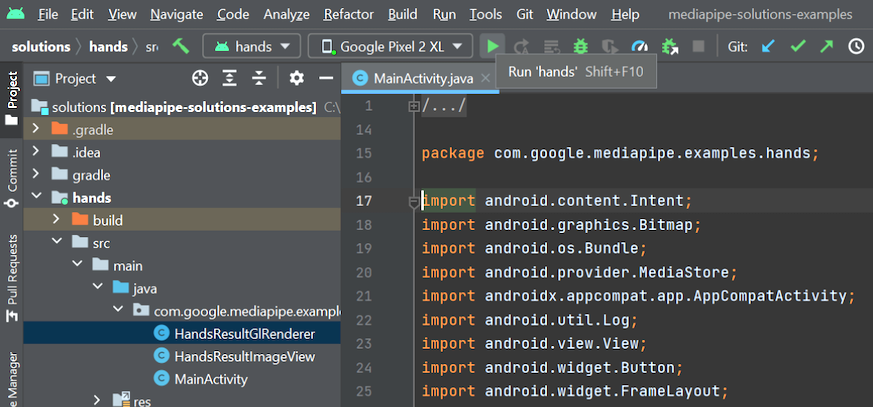
Run solution example app in Android Studio.
-
(Optional) Run solutions on CPU.
MediaPipe solution example apps run the pipeline and model inference on GPU by default. If needed, for example to run the apps on Android Emulator, set the
RUN_ON_GPUboolean variable tofalsein the app'sMainActivity.javato run the pipeline and model inference on CPU.
MediaPipe Solution APIs Terms of Service
Last modified: November 12, 2021
Use of MediaPipe Solution APIs is subject to the Google APIs Terms of Service, Google API Services User Data Policy, and the terms below. Please check back from time to time as these terms and policies are occasionally updated.
Privacy
When you use MediaPipe Solution APIs, processing of the input data (e.g. images, video, text) fully happens on-device, and MediaPipe does not send that input data to Google servers. As a result, you can use our APIs for processing data that should not leave the device.
MediaPipe Android Solution APIs will contact Google servers from time to time in order to receive things like bug fixes, updated models, and hardware accelerator compatibility information. MediaPipe Android Solution APIs also send metrics about the performance and utilization of the APIs in your app to Google. Google uses this metrics data to measure performance, API usage, debug, maintain and improve the APIs, and detect misuse or abuse, as further described in our Privacy Policy.
You are responsible for obtaining informed consent from your app users about Google’s processing of MediaPipe metrics data as required by applicable law.
Data we collect may include the following, across all MediaPipe Android Solution APIs:
-
Device information (such as manufacturer, model, OS version and build) and available ML hardware accelerators (GPU and DSP). Used for diagnostics and usage analytics.
-
App identification information (package name / bundle id, app version). Used for diagnostics and usage analytics.
-
API configuration (such as image format, resolution, and MediaPipe version used). Used for diagnostics and usage analytics.
-
Event type (such as initialize, download model, update, run, and detection). Used for diagnostics and usage analytics.
-
Error codes. Used for diagnostics.
-
Performance metrics. Used for diagnostics.
-
Per-installation identifiers that do not uniquely identify a user or physical device. Used for operation of remote configuration and usage analytics.
-
Network request sender IP addresses. Used for remote configuration diagnostics. Collected IP addresses are retained temporarily.